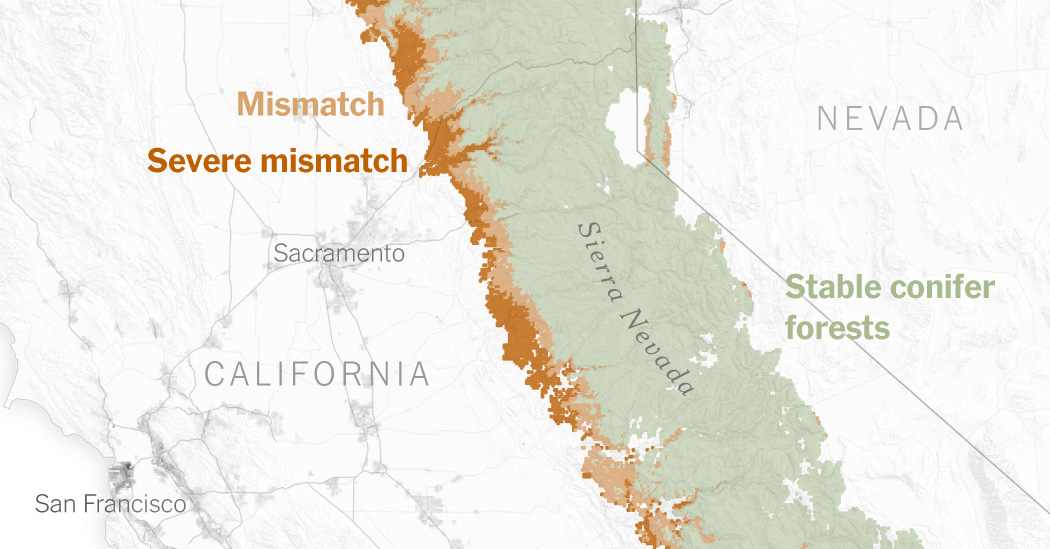
A warming local weather has left a fifth of the conifer forests that blanket California’s Sierra Nevada stranded in habitats that not swimsuit them, in keeping with a research revealed final week by researchers at Stanford College.
In these “zombie forests,” older, well-established timber — together with ponderosa pines, Douglas firs and sugar pines — nonetheless tower overhead, however few younger timber have been in a position to take root as a result of the local weather has develop into too heat and dry for them to thrive.
Lower than one % of conifer forests traditionally occurred in present local weather.
Lower than 5 % of conifer forests traditionally occurred in present local weather.
Lower than one % of conifer forests traditionally occurred in present local weather.
Lower than 5 % of conifer forests traditionally occurred in present local weather.
Lower than one % of conifer forests traditionally occurred in present local weather.
Lower than 5 % of conifer forests traditionally occurred in present local weather.
Supply: The World Ecology and Local weather Options Lab on the Stanford Woods Institute for the Atmosphere, utilizing knowledge from the U.S. Forest Service’s Wieslander Survey and Current Vegetation maps.
Word: The info appears to be like at modifications in conifer forests throughout the Sierra Nevada between the Nineteen Thirties and the 2010s.
Zombie forests are “dishonest dying, in a method,” mentioned Avery Hill, an ecologist and the research’s lead writer.
Mature timber are in a position to survive even after their native local weather has shifted, however the species just isn’t more likely to develop again in these areas after a serious disturbance, like a catastrophic wildfire, logging occasion or interval of utmost drought. As an alternative, the research discovered, the forest is extra probably to get replaced by smaller, shrublike vegetation that’s tailored to hotter, drier circumstances.
For his or her evaluation, Dr. Hill and colleagues examined historic knowledge going again greater than eight a long time, evaluating detailed survey knowledge plotted by the U.S. Forest Service within the Nineteen Thirties with newer vegetation maps. They discovered that in that point interval, the Sierra Nevada’s conifer forests had, on common, shifted about 112 ft greater in elevation. Essentially the most appropriate temperature vary for the conifers had shifted even quicker, climbing upslope by about 600 ft.
That has left an estimated 11 % of right now’s conifer forest within the Sierra Nevada mismatched to its present local weather circumstances, with one other 8 % thought-about “severely” mismatched, in keeping with the research, which was revealed within the journal PNAS Nexus. Dr. Hill was a doctoral pupil at Stanford on the time of the analysis.
World local weather change has put strain on many species of crops and animals to maneuver to greater elevations or towards polar latitudes as a way to keep in local weather zones they’ve traditionally tailored to. Longer-lived species, like conifer timber, which may dwell for hundreds of years, typically discover it more durable to maintain up with the speed of local weather change, mentioned Chris Area, the director of the Stanford Woods Institute for the Atmosphere and senior writer on the research. They’ll solely transfer as quick as their seeds get dispersed.
Hotter winters and drier summers can even embolden invasive bugs and illnesses to maneuver northward, killing some native crops and timber. Foresters in Rhode Island and throughout the nation have tried bold experiments to intentionally transfer sure tree species northward in a course of referred to as assisted migration.
Temperatures within the Sierra Nevada have warmed by a median of 1.2 levels Celsius (2.2 levels Fahrenheit) because the Nineteen Thirties. A warming local weather has exacerbated California’s “climate whiplash,” consultants say. Following years of drought, this yr noticed main storms that dumped document quantities of snow throughout the Sierras.
The current research ascribed climatic elements, together with modifications in annual precipitation and winter temperatures, as two main drivers of the shifts in appropriate conifer habitats. It additionally notes that wildfires and different disturbances, in addition to rising human presence in previously wild lands, have performed a task within the altering forests.
World warming “just isn’t all the story,” mentioned Jon Keeley, a analysis scientist with the US Geological Survey, who didn’t work on the research. The function of historic forest administration practices has additionally influenced the modifications in conifer forest distribution, he mentioned, because it has helped gasoline extra damaging wildfires.
Till the Nineteen Thirties, low-intensity fires that didn’t kill many giant timber occurred frequently, which meant tree seedlings may extra simply re-establish themselves in these areas after the hearth. Nevertheless, a long time of aggressive wildfire suppression that started within the twentieth century led to a buildup of vegetation in forests that was primed to burn. As soon as ignited, they typically resulted in higher-intensity “crown” fires that might unfold throughout a forest cover from treetop to treetop and go away huge swaths of the panorama barren and arid, making it tougher for younger timber to take root, Dr. Keeley mentioned.
People have additionally more and more moved into the fire-prone foothills of the Sierra Nevada. Fast growth in areas referred to as the “wildland-urban interface” has elevated wildfire threat.
Extra lately, forest managers have begun utilizing prescribed burns to preemptively skinny out forests in order that wildfires have much less gasoline to eat, however the altering local weather is making intentional burns extra sophisticated to hold out.
The Stanford group additionally mapped the place the conifer-dominated forests of the Sierra Nevada have already transitioned to landscapes dominated by different vegetation, like shrubs or flowering crops, between the Nineteen Thirties and the 2010s.
Areas which have remained dominated by conifers
Areas which might be not dominated by conifers
Some forest knowledge is lacking resulting from incomplete survey data
Areas which have remained dominated by conifers
Areas which might be not dominated by conifers
Some forest knowledge is lacking resulting from incomplete survey data
Supply: The World Ecology and Local weather Options Lab on the Stanford Woods Institute for the Atmosphere, utilizing knowledge from the U.S. Forest Service’s Wieslander Survey and Current Vegetation maps.
When transitions like this occur, it may possibly hurt native and native species which might be depending on the forests. Forests additionally play a crucial function in regulating water high quality and sequestering carbon.
The brand new research may help forest managers and policymakers prioritize their restricted assets, mentioned Winslow Hansen, an ecologist with the nonprofit Cary Institute of Ecosystem Research, who didn’t contribute to the research.
That would imply conserving zombie forests in mismatched areas for so long as doable, he mentioned, or directing assets to areas the place the local weather remains to be aligned with the vegetation.